
Hello friends in this blog I am going to write about Python,its installation,its comparisons with other languages and some thing about VPython as well as SciPY.
If you want to download the e-book for python download it from either clicking the picture or clicking the link given below
I am not a well experienced in python but I just want to share stuffs which I learnt over intenet.
All the informations in this Blog are written after verifications.
Lets Go...
WHAT IS PYTHON?
Python is the high-level programming language which concentrates more on its code readability.It uses indentation for block delimiters.Python is free and open source software.
INSTALLATION
UBUNTU/DEBIAN
sudo aptitude install python2.5
Windows XP:
python 2.6.4 for windows
BASICS
Python gives more concentrations on the structure and the indentation of the code so we need to be careful with respect to the indentation of the code.
FOR EXAMPLE
>>>if 1 + 1 == 2:
print "foo"
print "bar"
>>>if 1+2 == 3:
print "foo"
print "bar"
OUTPUT for the code is
hello.py
foo
bar
foo
bar
consider this code
>>>if 1 + 1 == 2:
print "foo"
print "bar"
>>> if 1+2 == 3:
print "foo"
print "bar"
OUTPUT
File "hllo.py", line 4
if 1 + 2== 2:
Thus Python gives more importance to the readability for the code.Python uses whitespace indentation, rather than curly braces or keywords, to delimit blocks.An increase in indentation comes after certain statements; a decrease in indentation signifies the end of the current block.
CASE-SENSITIVENESS
Python is case sensitive.So the careful usage is important.
STATEMENTS SUPPORTED
There are many statements supported by Python let me say some of them
* The if statement, which conditionally executes a block of code, along with else and elif (a contraction of else-if).
* The for statement, which iterates over an iterable object, capturing each element to a local variable for use by the attached block.
* The while statement, which executes a block of code as long as its condition is true.
* The try statement, which allows exceptions raised in its attached code block to be caught and handled by except clauses; it also ensures that clean-up code in a finally block will always be run regardless of how the block exits.
* The class statement, which executes a block of code and attaches its local namespace to a class, for use in object-oriented programming.
* The def statement, which defines a function or method.
* The with statement (from Python 2.6), which encloses a code block within a context manager (for example, acquiring a lock before the block of code is run, and releasing the lock afterwards).
* The pass statement, which serves as a NOP and can be used in place of a code block.
* The assert statement, used during debugging to check for conditions that ought to apply.
* The yield statement, which returns a value from a generator function.
* The print statement, which writes a value to an output stream
Functions usage:
Python uses def for defining a function it is much similar to that of the function keyword in c or c++
EXAMPLE
def add(a,b):
c=a+b
print c
def sub(a,b):
d=a-b
print d
add(3,4)
sub(5,7)
OUTPUT
7
-2
DATA TYPES
Despite being dynamically typed, Python is strongly typed, forbidding operations that are not well-defined (for example, adding a number to a string) rather than silently attempting to make sense of them.
CLICK ON THE IMAGE FOR BETTER VIEWING OF THE DATATYPES

COMPARISONS OF PYTHON WITH OTHER LANGUAGES
I don't have much knowledge on various languages so I found it in a site I share this with you
Java vs Python
1. interpreted vs. compiled is a big productivity win for Python
2. dynamic typing is a big productivity win for Python
3. Java is way faster than Python
4. minimal scaffolding is a big productivity win for Python. Makes programming more pleasant not to have to build all the infrastructure.
5. mostly first class functions a big win for Python.
6. built-in lists/arrays and hashes/dictionaries a big win over Java [] and library based collections. Java 5.0 fixes some of this but in Java collections still seem tacked on rather than integrated.
7. dynamic code loading in Python is a big win. Yes you can do it in Java but again, the cruft.
8. There is some weirdness in Python lexical scoping of names. The documentation for each has several warnings about edge cases where names don't bind in the expected way. This gives me a queasy feeling although in practice it may not matter. Another win for static type checking.
9. Java 'Comparable' interface ugly compared to Python built in comparison mechanisms that require only that a single function be implemented to get the full set of comparison operators. An example of excess Java scaffolding.
10. lack of multiline comments in Python was annoying
Fine in this you may or may not understand certain terms like DYNAMIC TYPING,SCAFFOLDING,dynamic code loading,multiline comments.If your comfortable with these terms you skip this else let me explain
DYNAMIC TYPING:
It is nothing but we can declare a variable without any data type but the value has the data type. For example in Python,if you need a variable, you simply come up with a name and start using it as a variable.
sam = 5 or sam = "hello";
SCAFFOLDING : This is the meta-programming method of building databases.Usally used in frameworks like Django which uses Python.It is nothing but a simple command to create a CRUD application
dynamic code loading:Automatic loading of script.Used both in java as well as python but python is better than java.
multiline comments:We cannot comment more than one line in Python.
LIBRARIES
Python has a large standard library, commonly cited as one of Python's greatest strengths,providing pre-written tools suited to many tasks.But let me say some of the library used for SCIENTIFIC PURPOSES and also developing 3-D models.
NumPy
NumPy is an extension to the Python programming language, adding support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a large library of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
example
x = linspace(0, 2*pi, 100)
y = sin(x)
plot(x, y)
show()
SciPy
SciPy is an open source library of algorithms and mathematical tools for the Python programming language.SciPy contains modules for optimization, linear algebra, integration, interpolation special functions, FFT, signal and image processing, ODE solvers and other tasks common in science and engineering. It has a similar audience to applications as MATLAB, GNU Octave, and Scilab.
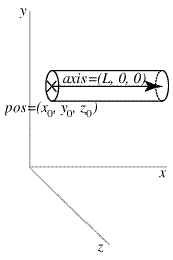
Vpython
VPython is the Python programming language plus a 3D graphics module called Visual. VPython allows users to create objects such as spheres and cones in 3D space and displays these objects in a window. Real-time, navigable 3D animations are generated as a side effect of computations. This makes it easy to create simple visualizations, allowing programmers to focus more on the computational aspect of their programs. The simplicity of VPython has made it a tool for the illustration of simple physics, especially in the educational environment.
from visual import * #import the visual module
rod = cylinder(pos=(0,2,1), axis=(5,0,0), radius=1)
We can learn more about Python by learning from e-books available over internet as well as from e-learning sites.
here are some:
http://docs.python.org/tutorial/
http://docs.python.org/release/2.3.5/tut/tut.html
http://www.scipy.org/Cookbook
e-books
DOWNLOAD THE E--BOOK FOR PYTHON
------------CLICK HERE---------------
Thank you...
No comments:
Post a Comment